"Most people living in the USA have no clue that the Internal Revenue Service (IRS) is a foreign agency.
To be more accurate, the IRS is a foreign private corporation of the International Monetary Fund (IMF) and is the private “army” of the Federal Reserve (Fed).
Its main goal is to make sure the American people pay their tax and be good little slaves."
This sermon will use other people's work along with the usual government websites that will document to you just how Corrupt this World is.
Who controls The International Monetary Fund?
The United Nations is the parent organization that handles the proper functioning and administration of the IMF. The IMF is headed by a Managing Director who is elected by the Executive Board for a 5-year term of office. The International Monetary Fund (IMF) consists of the Board of Governors, Ministerial Committees, and the Executive Board.
What is the IMF?
"The IMF was established in 1944 in the aftermath of the Great Depression of the 1930s. The Brentton Woods Monetary Conference: 44 founding member countries sought to build a framework for international economic cooperation. Today, its membership embraces 190 countries, with staff drawn from 150 nations.
The IMF is governed by and accountable to those 190 countries that make up its near-global membership.
The IMF's resources mainly come from the money that countries pay as their capital subscription (quotas) when they become members. Each member of the IMF is assigned a quota, based broadly on its relative position in the world economy. Countries can then borrow from this pool when they fall into financial difficulty."
International Monetary Fund serves to stabilize the international monetary system and acts as a monitor of the world’s currencies.
How is the IMF Organized?
"At the top of its organizational structure is the Board of Governors. The day-to-day work of the IMF is overseen by its 24-member Executive Board, which represents the entire membership and supported by IMF staff. The Managing Director is the head of the IMF staff and Chair of the Executive Board. S/he is assisted by four Deputy Managing Directors."
What are Captial Subscription quotas?

How Does the International Monetary Fund Provide Loans?
The IMF provides loans—including emergency loans—to member countries experiencing actual or potential balance of payments problems. The aim is to help them rebuild their international reserves, stabilize their currencies, continue paying for imports, and restore conditions for strong economic growth, while correcting underlying problems.
As we discussed in What is the World Bank, we learn that the World Bank and The International Monetary Fund go together. Here is how:
"Founded at the Bretton Woods conference in 1944, the two institutions have complementary missions. The World Bank Group works with developing countries to reduce poverty and increase shared prosperity, while the International Monetary Fund serves to stabilize the international monetary system and acts as a monitor of the world’s currencies. The World Bank Group provides financing, policy advice, and technical assistance to governments, and also focuses on strengthening the private sector in developing countries. The IMF keeps track of the economy globally and in member countries, lends to countries with balance of payments difficulties, and gives practical help to members. Countries must first join the IMF to be eligible to join the World Bank Group; today, each institution has 189 member countries."
To Learn More about the Formation of the World Bank and the IMF by Spies and Criminals:
To Find out about the Members of the International Monetary Fund
Next, we will be looking at the Board of Directors and the Role the United States Plays as the Governor of the IMF which is also the Secretary of Treasury.
Department of Treasury States:
"The IMF is an organization of 189 member countries that works to foster global monetary cooperation, secure financial stability, facilitate international trade, promote high employment and sustainable economic growth, and reduce poverty around the world.
The Secretary of the Treasury serves as the U.S. Governor to the IMF, and the U.S. Executive Director of the IMF is one of 24 directors who exercise voting rights over the strategic direction of the institution. The U.S. is the largest shareholder in the Fund."
Board of Governors
The Board of Governors consists of one governor and one alternate governor for each member country. Each member country appoints its two governors. The Board normally meets once a year and is responsible for electing or appointing an executive director to the executive board. While the Board of Governors is officially responsible for approving quota increases, special drawing right allocations, the admittance of new members, compulsory withdrawal of members, and amendments to the Articles of Agreement and By-Laws, in practice it has delegated most of its powers to the IMF's executive board.[86]
Executive Board
24 Executive Directors make up the executive board. The executive directors represent all 189 member countries in a geographically based roster.[88] Countries with large economies have their own executive director, but most countries are grouped in constituencies representing four or more countries.[86]
Following the 2008 Amendment on Voice and Participation which came into effect in March 2011,[89] seven countries each appoint an executive director: the United States, Japan, China, Germany, France, the United Kingdom, and Saudi Arabia.[88] The remaining 17 Directors represent constituencies consisting of 2 to 23 countries. This Board usually meets several times each week.[90] The Board membership and constituency is scheduled for periodic review every eight years.[9
So,24 people make decisions for 189 Countries and Billions of People? Look around, if they did their jobs, we would not be starving, we would have heat, we would be able to do things we and and go where we want and....
What Is The Department of Treasury's Position Internationally?
"The Treasury Department works with other federal agencies, foreign governments, and international financial institutions to encourage global economic growth, raise standards of living, and to the extent possible, predict and prevent economic and financial crises.
The Treasury Department also performs a critical and far-reaching role in enhancing national security by implementing economic sanctions against foreign threats to the U.S., identifying and targeting the financial support networks of national security threats, and improving the safeguards of our financial systems. Treasury's Office of International Affairs works on a wide range of economic issues. Following are links to additional information about international economic issues, institutions, and priority policy areas."
Let us look at the links for the additional information so we can learn truth.
The Committee on Foreign Investment in the United States (CFIUS) is an inter-agency committee authorized to review certain transactions involving foreign investment in the United States, in order to determine the effect of such transactions on the national security of the United States
The Exchange Stabilization Fund (ESF) consists of U.S. dollars, foreign currencies, and Special Drawing Rights and can be used to purchase or sell foreign currencies, to hold U.S. foreign exchange and Special Drawing Rights (SDR) assets, and to provide financing to foreign governments. All operations of the ESF require the explicit authorization of the Secretary of the Treasury who is responsible for the formulation and implementation of U.S. international monetary and financial policy, including exchange market intervention policy.
The Exchange Stabilization Fund (ESF) consists of three types of assets: U.S. dollars, foreign currencies, and Special Drawing Rights (SDRs), which is an international reserve asset created by the International Monetary Fund.
The ESF can be used to purchase or sell foreign currencies, to hold U.S. foreign exchange and Special Drawing Rights (SDR) assets, and to provide financing to foreign governments. All operations of the ESF require the explicit authorization of the Secretary of the Treasury ("the Secretary").
The Secretary is responsible for the formulation and implementation of U.S. international monetary and financial policy, including exchange market intervention policy. The ESF helps the Secretary to carry out these responsibilities. By law, the Secretary has considerable discretion in the use of ESF resources.
The legal basis of the ESF is the Gold Reserve Act of 1934. As amended in the late 1970s, the Act provides in part that "the Department of the Treasury has a stabilization fund …Consistent with the obligations of the Government in the International Monetary Fund (IMF) on orderly exchange arrangements and an orderly system of exchange rates, the Secretary …, with the approval of the President, may deal in gold, foreign exchange, and other instruments of credit and securities.
What are Instruments of Credit and Securites?
Credit Securities means fixed-income securities, debt securities and loans and investments with economic characteristics similar to fixed-income securities, debt securities and loans issued by entities other than the U.S. Government, including corporate bonds, loans and loan participations, asset-backed securities (all or a portion of which may consist of collateralized loan obligations), mortgage-backed securities (both residential mortgage-backed securities and commercial mortgage-backed securities), mezzanine and preferred securities, convertible securities, commercial paper, municipal securities and sovereign government and supranational debt securities.
Examples of Instruments of Credit
Mortgage-backed securities are a type of bond in which an investor buys a mortgage from a mortgage lender. When all goes well, an MBS investor collects monthly mortgage payments until the loan is fully repaid, but there is the risk of default.
What is a morgatge?
a legal agreement by which a bank or other creditor lends money at interest in exchange for taking title of the debtor's property, with the condition that the conveyance of title becomes void upon the payment of the debt:
This is how China and other countries are buying our land. We are paying our debts back with mortgage-backed securities.
According to a report by the American Enterprise Institute, China now owns more than 1.2 million acres of land in the United States. This includes nearly 700,000 acres of farmland and nearly 500,000 acres of commercial and industrial property.
Promissory Note: The Federal Reserve
The simplest form of a credit instrument is the promissory note. A promissory note (or pro-note for short) is a written promise from a buyer or a borrower to pay a certain sum of money to the creditor or his order. It is what we call IOU (I owe you), i.e., an acknowledgment of debt and an obligation to repay.
Technically, yes, a federal reserve note is a promissory note that does not pay any interest. It is defined as such because it states that "this note is legal tender for all debts, public and private," indicating a promise for the government and private citizens to accept and honor the note as legal tender.
Federal Reserve notes are no longer backed by assets such as gold. Instead, Federal Reserve notes are supported solely by the government's declaration that "this note is legal tender for all debts, public and private" in the United States.
Today, Federal Reserve notes circulate as money throughout the U.S. and the rest of the world wherever dollar-denominated transactions take place. These notes are still commonly referred to as "dollars," which was previously a legally defined quantity of gold or silver but is now simply the official unit of account for U.S. legal tender, including Federal Reserve notes.
The U.S. Treasury prints the Federal Reserve notes at the instruction of the Board of Governors and the 12 Federal Reserve member banks. These banks also act as the clearinghouse for local banks that need to increase or reduce their supply of cash on hand. Once new Federal Reserve notes are issued, they become a liability of the Federal Reserve, which can be redeemed by bearers on demand for different Federal Reserve notes.
Recall what the Board of Governors Means-The International Monetary Fund.
"At the top of its organizational structure is the Board of Governors. The day-to-day work of the IMF is overseen by its 24-member Executive Board, which represents the entire membership and supported by IMF staff. The Managing Director is the head of the IMF staff and Chair of the Executive Board. S/he is assisted by four Deputy Managing Directors."
What Is the International Reserves?
International reserves (or reserve assets in the balance of payments) are those external assets that are readily available to and controlled by a country’s monetary authorities. According to the International Monetary Fund (IMF), international reserves comprise foreign currencies, other assets denominated in foreign currencies, gold reserves, special drawing rights (SDRs) and IMF reserve positions. These reserves may be used for direct financing of international payments imbalances, or for indirect regulation of the magnitude of such imbalances via intervention in foreign exchange markets in order to affect the exchange rate of the country’s currency. A narrower definition for international reserves only includes foreign currency deposits and bonds. These assets held by the country’s monetary authorities are usually denominated in different reserve currencies, mostly the U.S. dollar (USD), the Euro (EUR), the Japanese yen (JPY) and the British pound (GBP).
To understand this we must Learn about what THE EXTERNAL WEALTH OF NATIONS (EWN) MEASURES?
The EWN provides estimates of each country’s external financial assets and liabilities. These data also yield estimates of each country’s net international investment position (NIIP), the difference between its total external financial assets and its total external liabilities.
External Assets
foreign direct investment (controlling stakes by domestic firms in overseas’ affiliates);
portfolio investment (holdings by domestic residents of stocks or bonds issued by nonresident entities);
other investment (including loans to or deposit in nonresident entities, trade credits, etc);
financial derivatives;
foreign exchange reserves (holdings of liquid foreign-currency assets by the domestic central bank).
Financial liabilities are defined analogously (with the exception of foreign exchange reserves—any liability of the central bank vis-à-vis nonresidents is classified in the liability category corresponding to the nature of such liability). For example, if a U.S. firm has a controlling interest in an Irish firm domiciled in Ireland, that is an external asset of the U.S. and an external liability of Ireland. Similarly, if an Irish individual holds stock in a U.S. firm, that’s an external asset of Ireland and an external liability of the U.S.
Next we need to understand the Treasury Departments Role with the Federal Reserve
The Secretary of the Treasury is the chief international monetary policy official of the United States. The Federal Reserve has separate legal authority to engage in foreign exchange operations. The Federal Reserve's foreign exchange operations are conducted in close and continuous consultation and cooperation with the Secretary to ensure consistency with U.S. international monetary and financial policy.
The Treasury and the Fed have closely coordinated their foreign exchange operations since early 1962, when the Federal Reserve commenced such operations at the request of the Treasury. Operations are conducted through the Federal Reserve Bank of New York (FRBNY), as fiscal agent of the United States and as the operating arm of the Federal Reserve System.
What is the Federal Reserve System?
The Federal Reserve System (often shortened to the Federal Reserve, or simply the Fed) is the central banking system of the United States of America. It was created on December 23, 1913, with the enactment of the Federal Reserve Act , after a series of financial panics (particularly the panic of 1907 ) led to the desire for central control of the monetary system in order to alleviate financial crises.
What Does The Fed Do?
Conducting the nation's monetary policy by influencing money and credit conditions in the economy in pursuit of full employment and stable prices.
Supervising and regulating banks and other important financial institutions to ensure the safety and soundness of the nation's banking and financial system and to protect the credit rights of consumers.
Maintaining the stability of the financial system and containing systemic risk that may arise in financial markets.
Providing certain financial services to the U.S. government, U.S. financial institutions, and foreign official institutions, and playing a major role in operating and overseeing the nation's payments systems.
Definition of Influence
the capacity to have an effect on the character, development, or behavior of someone or something, or the effect itself: "the influence of television violence"
Foreign exchange reserves are assets held on reserve by a central bank in foreign currencies. These reserves are used to back liabilities and influence monetary policy. It includes any foreign money held by a central bank, such as the U.S. Federal Reserve Bank.
As you can see the Federal Reserve is the Central bank that oversees the nation's payments system so that they can pay whomever the Treasury Department States based upon What the International Monetary Fund wants to support for the greater good of the world and What has done what for all of us? Especially when we are selling our land to China, our Money is worthless and Printed on Demand, not to mention that this crime ring is ran by 24 Members Representing the Best Interests of 190 countries and Billions of People.

Why was the IRS Formed?
The IRS mission is to provide America's taxpayers top quality service by helping them understand and meet their tax responsibilities and to enforce the law with integrity and fairness to all.
Statutory Authority
We're organized to carry out the responsibilities of the Treasury secretary per Internal Revenue Code (IRC) Section 7801. The IRS was created based on the secretary's authority to administer and enforce the internal revenue laws.
26 U.S.C. § 7801 - U.S. Code - Unannotated Title 26. Internal Revenue Code § 7801. Authority of Department of the Treasury
(a) Powers and duties of Secretary. --
(1) In general. --Except as otherwise expressly provided by law, the administration and enforcement of this title shall be performed by or under the supervision of the Secretary of the Treasury.
2) Administration and enforcement of certain provisions by Attorney General. --
(A) In general. --The administration and enforcement of the following provisions of this title shall be performed by or under the supervision of the Attorney General; and the term “Secretary” or “Secretary of the Treasury” shall, when applied to those provisions, mean the Attorney General; and the term “internal revenue officer” shall, when applied to those provisions, mean any officer of the Bureau of Alcohol, Tobacco, Firearms, and Explosives so designated by the Attorney General: (i) Chapter 53. (ii) Chapters 61 through 80, to the extent such chapters relate to the enforcement and administration of the provisions referred to in clause (i). (B) Use of existing rulings and interpretations. --Nothing in this Act 1 alters or repeals the rulings and interpretations of the Bureau of Alcohol, Tobacco, and Firearms in effect on the effective date of the Homeland Security Act of 2002, which concern the provisions of this title referred to in subparagraph (A). The Attorney General shall consult with the Secretary to achieve uniformity and consistency in administering provisions under chapter 53 of title 26, United States Code.
[(b) Repealed. Pub.L. 97-258 , § 5(b) , Sept. 13, 1982, 96 Stat. 1068, 1078]
(c) Functions of Department of Justice unaffected. --Nothing in this section or section 301(f) of title 31 shall be considered to affect the duties, powers, or functions imposed upon, or vested in, the Department of Justice, or any officer thereof, by law existing on May 10, 1934.
internal revenue officer
(2) Administration and enforcement of certain provisions by Attorney General
(A) In general The administration and enforcement of the following provisions of this title shall be performed by or under the supervision of the Attorney General; and the term “Secretary” or “Secretary of the Treasury” shall, when applied to those provisions, mean the Attorney General; and the term “internal revenue officer” shall, when applied to those provisions, mean any officer of the Bureau of Alcohol, Tobacco, Firearms, and Explosives so designated by the Attorney General: (i) Chapter 53. (ii) Chapters 61 through 80, to the extent such chapters relate to the enforcement and administration of the provisions referred to in clause (i).
(B) Use of existing rulings and interpretations Nothing in the Homeland Security Act of 2002 alters or repeals the rulings and interpretations of the Bureau of Alcohol, Tobacco, and Firearms in effect on the effective date of such Act, which concern the provisions of this title referred to in subparagraph (A).
The Attorney General shall consult with the Secretary to achieve uniformity and consistency in administering provisions under chapter 53 of title 26, United States Code .
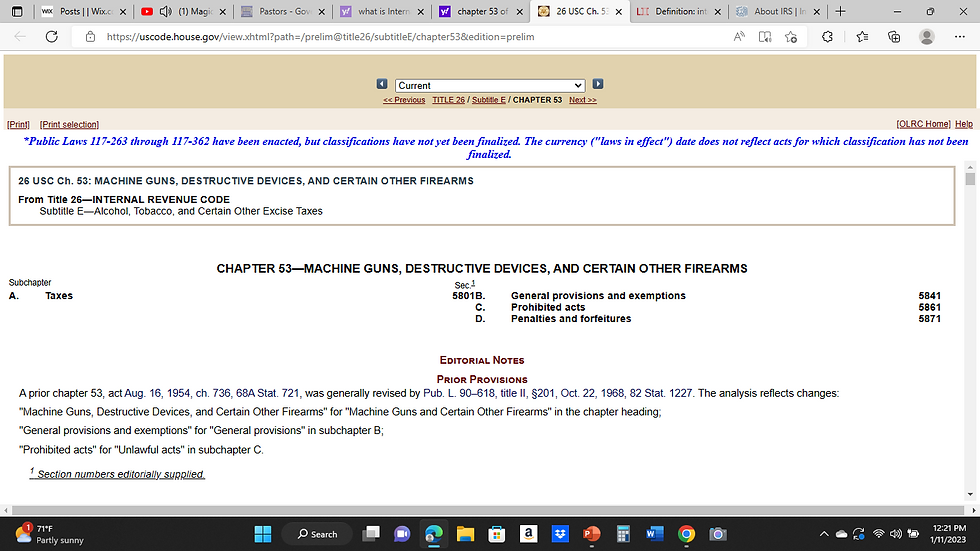
If You don't understand that the New IRS agents are employed to grab your guns and take our rights away, then I pray that you soon will.


Comentarios